

Nine of the sixteen are individuals who are dominant for both traits, six are individuals who are dominant for one trait and recessive for the other, and the single. Dominant allele- produces the same phenotype either paired or identical or different. Recessive- organism that has a recessive trait. Thus, because of the Law of Dominance, its more likely that the child would have a widows peak. When examining two autosomal dominant traits, a cross between two heterozygous individuals will always produce F1 offspring in the same 9:3:3:1 ratio. Dominant - an allele that produces the same phenotypic effect in heterozygotes and homozygotes. Lastly, males and females are equally likely to receive a dominant allele and express the trait. Having a widows peak is a dominant trait, while having a straight hairline is recessive. Dominantly inherited traits do not skip generations. Every affected individual must have an affected parent. A Punnett square can be used to determine all possible genotypic combinations in the parents.Ī pedigree that depicts a dominantly inherited trait has a few key distinctions. For example, if one parent is homozygous dominant (WW) and the other is homozygous recessive (ww), then all their offspring will be heterozygous (Ww) and possess a widow’s peak. If both parents are heterozygous (Ww), there is a 75% chance that any one of their offspring will have a widow’s peak (see figure). Only ww individuals will have a straight hairline. To determine the probability of inheritance of a widow’s peak (or any other dominant trait), the genotypes of the parents must be considered. An individual with a (WW) or (Ww) genotype will have a V-shaped peak at the hairline. The main difference between dominant and recessive genes is that the dominant genes always express the dominant trait whereas the recessive genes express the recessive trait. Let (W) represent the dominant allele, and (w) represent the recessive allele. One example of a dominantly inherited trait is the presence of a widow’s peak (a V-shape) at the hairline.
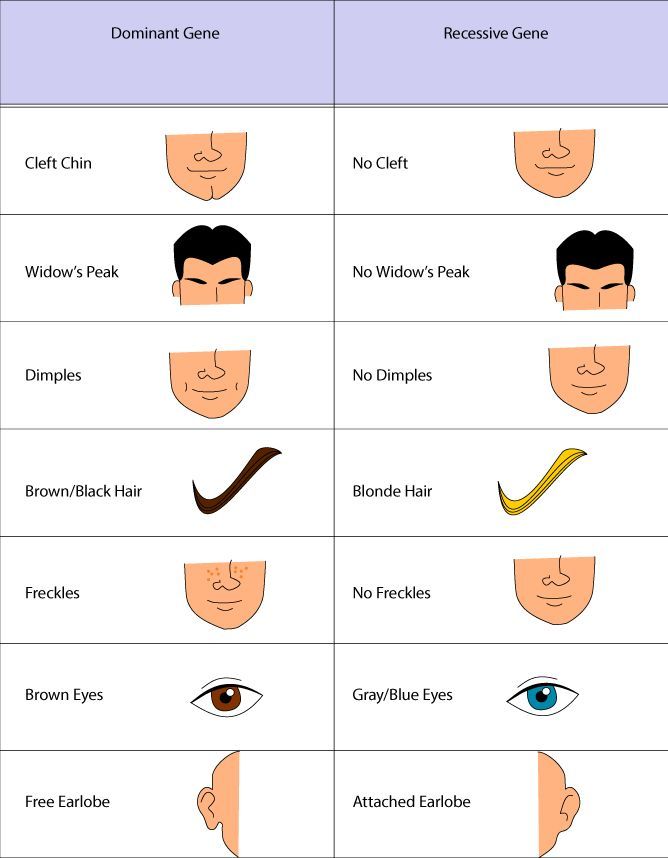
Offspring whose genotype is either AA or Aa will have the dominant trait expressed phenotypically, while aa individuals express the recessive trait. Since each parent provides one allele, the possible combinations are: AA, Aa, and aa. A dominant allele is denoted by a capital letter (A versus a). A dominant allele will mask a recessive allele, if present. When a trait is dominant, only one allele is required for the trait to be observed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
